
What's Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts and blocks users from accessing files, applications or systems. Through the above methods, the victim can be extorted to pay a ransom to regain the permissions or files, otherwise the access permissions may be lost forever.
Ransomware has become more and more active in recent years. According to data from the information security research company CyberSecurity Ventures, by 2021, companies will be attacked by ransomware every 11 seconds. The annual global cost of ransomware damage will reach US$20 billion. The average ransom and self-recovery costs also came to 12,000 and 64,000 US dollars. As the cost of repairing gets higher and higher, all units should pay more attention to the prevention of ransomware.
UPAS NOC: Deploy Defense Mechanisms Against Ransomware
For more details, please check the download link: UPAS NOC 7.0 Ransomware Protection
Types of Ransomware
In addition to the recent common file encryption, there are three main types of ransomware, such as threatening software and screen kidnapping.
Threatening Software
Through counterfeit security software, the user’s computer is constantly threatened with viruses, which require payment to register to remove; or disguise computer lock software to prevent others from using the computer at will. After a period of use, it will threaten the user if they do not pay Erase the files in the computer, but the files have not suffered any damage.
Screen Kidnapping Software
When this malicious software enters the computer, it will make the computer unusable, and a full-screen message will pop up to inform the user that the government unit has blocked the computer for illegal actions and needs to pay a fine to restore the right to use.
File Encryption Software
The oldest, most common and most dangerous type of ransomware is non-file encryption. Once the file is encrypted, there is almost no way to crack the encrypted file except for the backup file recovery. And there is no guarantee that the kidnappers will unlock the files as scheduled.
History of Ransomware
AIDS
The first ransomware that appeared in the world was the "AIDS Trojan" or "PC Cyborg" in 1989. It will encrypt all data in the C slot after the computer is restarted 90 times, and demand a ransom of $189 to be paid PC Cyborg Corporation to decrypt the files. This malware was created by Joseph Popp and distributed during the World Health Organization's (WHO) AIDS conference by distributing floppy disks disguised as AIDS data. Because the encryption method of the malware stores the password in the code, the AIDS Trojan was quickly cracked.

Gpcode
Over the next few years, ransomware gradually became active. In 2005, Gpcode was the first to use a more complex RSA encryption method to encrypt files, enticing users to download and run software through emails, then copy and encrypt the files and delete the original files. Although the length of the key used is short to make it easy to crack, it increases the difficulty of cracking compared to。
WinLock
It appeared widely in Russia in 2007 and became the first malicious software to be kidnapped on the screen. WinLock will kidnap the user’s computer screen, play pornographic images, and ask the user to pay the ransom via SMS.
Reveton
In 2012, when a new screen kidnapping software appeared, Reveton would display a forged notification from law enforcement agencies on the screen, pretending that the computer was blocked for participating in illegal network activities and required to pay a fine to resume use.
CryptoLocker
The file encryption ransomware came into a new process in 2013. CrytoLocker uses 2048-bit RSA encryption and requires the use of virtual currency as a way to pay the ransom. Not only does it increase the difficulty of cracking the key, it also reduces the possibility of tracking the murderer through the cash flow.
WannaCry
In May 2017, WannaCry ransomware broke out all over the world. WannaCry used Microsoft’s patched vulnerabilities - "Eternal Blue" - to attack, seeing that most users do not have the habit of updating, using vulnerabilities to spread rapidly on devices in the same area network. It is designed to target large Ransomware that the company attacks.
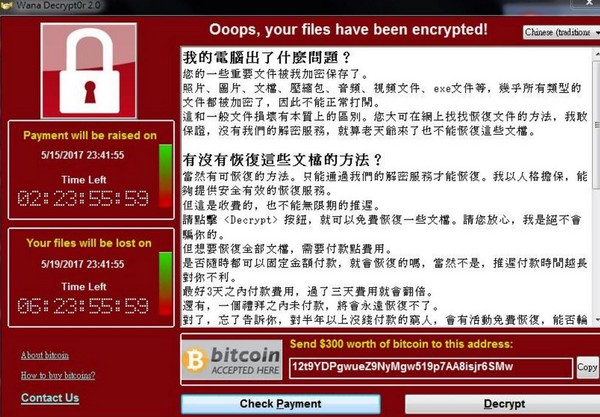
Petya
Petya first appeared in 2016 and had fewer infections than other malware at the time. However, in June 2017, Petya's variant "NotPetya" used the Eternal Blue vulnerability to carry out large-scale attacks like WannaCry. It infected the United States and European countries and mainly targeted Russia and Ukraine. It was the first to target energy companies, power grids, and gas stations. Ransomware that attacks infrastructure such as airports and banks. NotPetya is considered to be sabotage with a political purpose rather than a ransom, because NotPetya did not write a key upload module to the hacker's server.
After WannaCry and Petya, ransomware moved from infecting personal computers to one-time infections of large-scale equipment, such as government agencies, infrastructure, and manufacturing. In this way, a larger amount of ransom can be extorted.
Entry Points

The outbreak of new COVID-19 has changed the type of work, and the rate of remote workers has gradually increased. Remote work protects the lives of employees, but at the same time it brings a crisis of corporate information security. According to the Coveware survey, which specializes in providing consultation services for ransomware victims, the main intrusion channel for ransomware is remote desktop protocol, followed by phishing, and finally by exploiting software and OS version vulnerabilities.
Remote Desktop Protocol
The Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft that allows users to connect to the computer with other devices through the network to perform remote management.
Hackers can use the same channel to gain access to the computer by using leaked RDP credentials or brute force cracking. When the hacker enters the computer, he can perform any operation, including changing the password, installing malicious programs, burying backdoor programs, etc.
Most companies do not have comprehensive policies on passwords, making the password strength insufficient, and hackers can easily enter the internal network for damage. Therefore, RDP has become one of the main channels for hackers to attack.
Phishing & Email Phishing
As a channel widely used by hackers in the past, it is still one of the methods of hacker attacks. By sending fake e-mails or creating fake websites, hackers can trick victims into downloading and running malicious programs, thereby controlling computers to spread viruses or blackmail.
Website, Application, OS Vulnerability
Although hackers rarely use websites, applications, and OS version vulnerabilities to attack. Hackers can take advantage of system vulnerabilities such as Flash Player and Windows to gain control of the computer or insert files, and then further damages.
Propagation Mode
After the hacker gains control of the computer, he installs the ransomware on each terminal device through the following methods:

GPO Delivery
When a hacker gains control of a computer, he usually does not launch an attack on the computer immediately. Instead, he uses it as a springboard to obtain the highest authority account of the company's intranet AD, and then tamper with the GPO policy distribution and force each computer to execute Malicious program, and then kidnap files of all devices in the company.
Server Message Block SMB
SMB is a network file sharing protocol that uses port 139/TCP and port 445/TCP, allowing multiple PCs on the network to share files, printers and other resources together. SMB vulnerabilities are often used by hackers as a channel to spread viruses on the intranet.
For example, WannaCry and Petya in 2017 used a vulnerability called "Eternal Blue" 445/TCP port to spread across the world. Although this vulnerability has been patched by Microsoft a long time ago, most users have no habit of updating, which gives hackers the opportunity to invade.
A new SMB vulnerability was revealed in 2020. Through an attack on SMB, arbitrary programs can be executed on the target Windows 10. Although the vulnerability did not cause serious impact this time, it also reminded the importance of the update again.
Recent Cases in Taiwan
TSMC
In August 2018, TSMC was attacked by ransomware. A total of 5 factories were affected and a total loss of approximately 5.2 billion yuan. For example, technology leaders such as TSMC should have complete information security protection. Why are they still getting ransomware into the intranet for damage?
The cause of the incident was that TSMC was installing new equipment, and one of the employees did not perform anti-virus operations before connecting the new equipment to the network. So the ransomware virus was immediately sent to the TSMC intranet when the new equipment was connected to the network. The spread among the equipment spread to all the factories in Taiwan within a few hours.
Because a human error caused billions of losses, it can be seen that the damage caused by ransomware cannot be taken lightly.
CNPC, Formosa Plastics
In mid-2020, CNPC, Formosa Plastics and many other companies were attacked by ransomware. In this attack, it was discovered that the hackers had been in various corporate networks for a long time, and gradually obtained the system's highest authority account during this time. According to the investigation, the hacker carried out the first action on April 26, installing the backdoor program on the network management computer. Between May 4 and 5, hackers used the highest authority account to set up new GPO delivery content. When the computer is turned on, it will automatically download the ransomware. Then when the set time comes, all computers will be encrypted at the same time.
This incident caused not a small loss to the enterprise, but also caused inconvenience to people's lives. APT latent attacks are becoming more and more common, and how to detect potential information security risks in time has become one of the items that enterprises should pay attention to.
UPAS NOC: Deploy Defense Mechanisms Against Ransomware
For more details, please check the download link: UPAS NOC 7.0 Ransomware Protection

